
A practical die combination for the linear Mooney correction is using capillaries such as L/D=40/2 mm and L/D=20/1 mm. The following diagram shows a Bagley plot with this combination of capillaries.ĭue to this correlation, measurements at constant shear stress have to be made with capillaries of different diameter, but with the same L/D ratio. However, nonlinearities cannot be detected. If the inlet pressure loss is determined with only two capillaries, the combination L/D=20/1 mm and L/D=0.2/1 mm is favorable. It is essential that the shortest capillary is not too far from zero in length and the capillary lengths are not too close together to avoid extrapolation errors.Ī practical combination for the linear Bagley correction is given by using the capillaries L/D=30/1 mm, 20/1 mm and 10/1 mm.Ī favorable combination for a nonlinear Bagley correction is given by using the capillaries L/D=20/1 mm, L/D=10/1 mm and L/D=5/1 mm. Before the evaluation, at least two measurements with capillaries of the same diameter, but different lengths, must be carried out. To determine the inlet-outlet pressure loss, the pressure loss is plotted for different capillaries of the same diameter, but with different lengths and extrapolated to zero (Bagley plot).
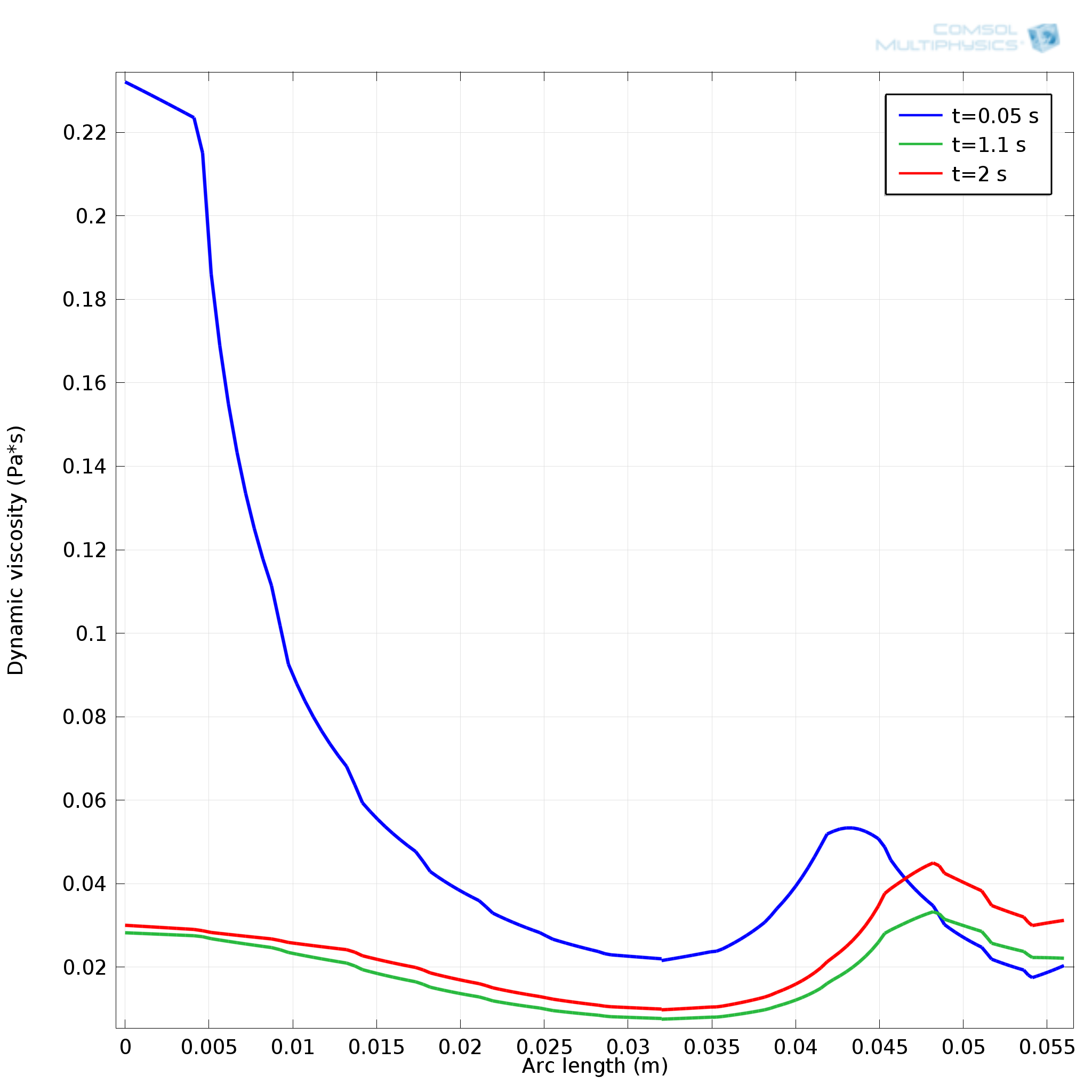

Using the Bagley correction, the viscous pressure drop in the capillary is separated from the pressure losses due to run-in and run-out effects.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
